CBD Oil: How Does it Work?
CBD Oil: How Does it Work?
Over the past few years, CBD oil has been gaining popularity. Several studies show that it has many health benefits, from helping lessen chronic pain to reducing anxiety. But how does it work? What makes it so beneficial to health and wellness? To answer this, we first need to understand how CBD works in our bodies.
How Does CBD Work?
Cannabidiol (CBD) is a naturally-occurring chemical compound present in cannabis plants, particularly hemp and marijuana. It is one of more than 100 cannabinoids that are present in various concentrations in cannabis. In particular, CBD is a major phytocannabinoid, accounting for up to 40% of the Cannabis Sativa L extract.
Most people prefer to consume CBD through CBD oil. This form comes from the flowers, leaves, and stalks of the cannabis plant. Manufacturers extract the oil through a process called CO2 extraction. After that, they mix the CBD extract with oils such as MCT, hemp, or coconut oil to make it more palatable.
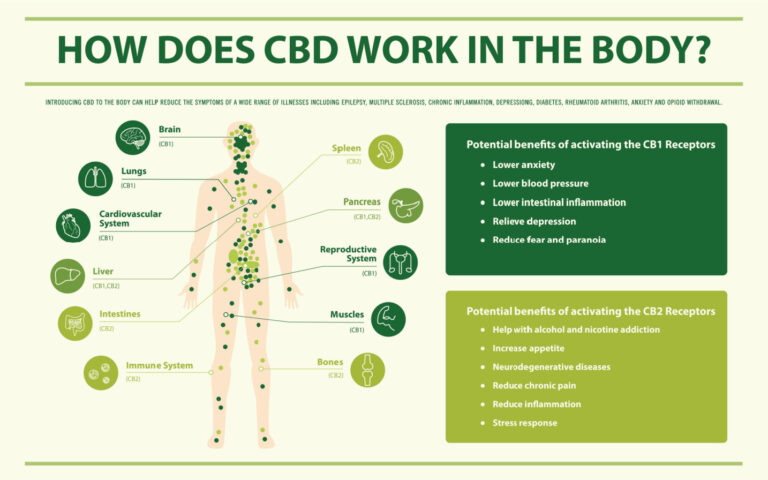
Cannabidiol Works With the Human Endocannabinoid System
The endocannabinoid system helps regulate many other systems in the body, such as pain sensation, mood, memory, and appetite. The ECS responds to internal and external signals from the environment, including:
stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline;
neurotransmitters like serotonin; and
other chemicals in your body, such as taste or smell compounds used when you eat food or drink coffee.
Like other cannabinoids, CBD interacts with your body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS). When you take CBD, it binds with receptors in your nervous system that are responsible for these processes. This allows you to experience some of the effects of cannabidiol.
CBD Oil Effects on Homeostasis
The most vital function of the endocannabinoid system is maintaining homeostasis throughout your body. The term ‘homeostasis’ refers to the ability of living things to maintain equilibrium in their internal environments. In other words, it refers to the system’s ability to sustain a healthy level of physical and chemical balance.
Essentially, when our bodies suffer from something—such as an injury or discomfort—our endocannabinoid system tries to bring things back into their normal function. Another example is when you eat spicy foods. In response to this discomfort, your body produces more saliva, which cools down the temperature in your mouth.
A particularly promising area of research is CBD’s effect on homeostasis, which may help your body regulate its systems more effectively. When CBD enters your system, it interacts with receptors within the ECS, which leads to therapeutic effects, including:
reducing pain and inflammation
lessening anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues
regulating sleep patterns
promoting better immune function
may be a useful adjunct therapy in other health conditions like cancer, diabetes, and heart disease.
These therapeutic effects happen because CBD activates serotonin levels in your brain. Serotonin helps regulate your moods, so if you have low serotonin levels, it could cause depression or anxiety. For pain, CBD primarily inhibits the neuronal transmission in pain pathways, which increases tolerance to pain
Moreover, this cannabinoid also has antioxidant properties. This means that it can help protect against free radicals in your body. The presence of free radicals results in oxidative stress, which quickly ages the cells and increases the risk of other diseases.
Does CBD Oil Get You High?
You won’t get high from CBD oil because it’s non-psychoactive.
The cannabinoid THC is responsible for getting you high. It’s psychoactive, meaning it affects your brain chemistry by binding with receptors in your brain and altering its normal functioning. This reaction can produce different effects on people depending on their genetics or tolerance level. For example, some people may experience intense relaxation while others may feel anxious or paranoid.
In addition, some products can contain trace amounts of THC. By dry weight, products containing delta-9 THC must be less than .3% delta-9 THC to comply with the 2018 U.S. Farm Bill. This condition makes CBD derived from hemp legal in most states and may not have significant psychoactive effects.
Do CBDs Work Without THC?
Let’s begin by discussing the “entourage effect,” a concept by Dr. Ethan Russo. This concept asserts that cannabinoids are more effective together than alone. CBD and traces of THC have a synergistic relationship when present in the same product.
Unlike CBD isolates, full-spectrum CBD products contain all the cannabinoids present in hemp plants and trace levels of THC. As we’ve said, hemp-derived CBD oil won’t give you significant psychoactive effects or “high.” However, THC enhances the body’s ability to absorb and process CBD, thereby increasing some of its benefits.
Does this mean that CBD without THC is still worth buying? Yes. A CBD oil without THC (CBD isolate) is still beneficial.
A great deal of discussion still surrounds the entourage effect—with some consumers believing this to be true while others maintain that pure CBD isolates are just as effective. So, it is totally your choice whether you prefer full-spectrum CBD oil or an isolate. Above all, it is crucial to choose a reputable manufacturer that provides transparent laboratory results.
Is CBD Addictive?
A report by the WHO (World Health Organization) shows that CBD does not seem to pose an addiction or abuse risk. In contrast to marijuana, it does not produce a high, which means it cannot be abused. Some evidence indicates that CBD may help reduce opiate and tobacco cravings in some circumstances. Preliminary studies also suggest that CBD may have potential as a treatment for substance use disorder.
Can You Overdose on CBD?
Unlike other substances with life-threatening effects, you can’t overdose on CBD. But side effects are possible if you consume too much or use a substandard product. The most common ones include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dizziness, and fatigue.
Moreover, CBD can interact with certain medications, so it’s important to know what you are taking and how it might affect your body. Suppose the side effects worsen after taking more than recommended doses, or you start to feel uncomfortable. When that happens, it’s better to stop and talk with your doctor about alternative options that could work more effectively for you.
How Long Do CBDs Stay in Your System?
Cannabidiol is fat-soluble, which means it stays in your body longer than water-soluble drugs like alcohol and caffeine, which leave your body within a few hours.
The length of time CBD stays in your body depends on:
the frequency you use CBD oil
amount of product you take
the method for consuming CBD (oils, tinctures, lotions, vapes, etc.)
how well your body metabolizes it
If you take CBD on a daily, the longer it will remain in your system. Based on a 2005 study, taking 1.35 milligrams of CBD left traces in the blood for around six hours after consumption, but higher doses remained longer.
The CBD product you choose will also contribute to how long it stays in your system. As per a 2018 review, smoking and inhaling CBD speed up the process of CBD entering the bloodstream and expelling it quicker. CBD oil, on the other hand, can stay in your system for several days (2-5 days) after you take it.
Takeaway
We hope this article provided a good insight into the science behind CBD oil. Even though more research is still underway, and there is still much to learn about how CBD works in the body, there is enough to say it has positive effects on health. You can find more information about CBD in our blog.


